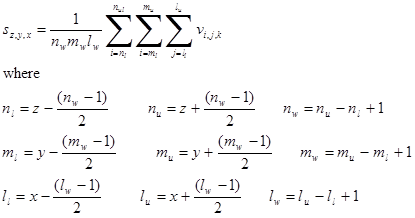| Constructors
|
public ThreeDimensionalSmooth(double[] xData, double[] yData, double[] zData, double[][][] vData)
|
| public ThreeDimensionalSmooth(double[][][] vData)
|
| public ThreeDimensionalSmooth(float[] xData, float[] yData, float[] zData, float[][][] vData)
|
| public ThreeDimensionalSmooth(float[][][] vData)
|
| public ThreeDimensionalSmooth(long[] xData, long[] yData, long[] zData, long[][][] vData)
|
| public ThreeDimensionalSmooth(long[][][] vData)
|
| public ThreeDimensionalSmooth(int[] xData, int[] yData, int[] zData, int[][][] vData)
|
| public ThreeDimensionalSmooth(int[][][] vData)
|
| public ThreeDimensionalSmooth(BigDecimal[] xData, BigDecimal[] yData, BigDecimal[] zData, BigDecimal[][][] vData)
|
| public ThreeDimensionalSmooth(BigDecimal[][][] vData)
|
| public ThreeDimensionalSmooth(BigInteger[] xData, BigInteger[] yData, BigInteger[] zData, BigInteger[][][] vData)
|
| public ThreeDimensionalSmooth(BigInteger[][][] vData)
|
| Smoothing
| Savitzky-Golay |
Smoothed Curves |
public double[][][] savitzkyGolay(int sgFilterWidthx, int sgFilterWidthy, int sgFilterWidthz)
|
| public double[][][] savitzkyGolay(int sgFilterWidth)
|
| public double[][][] getSavitzkyGolaySmoothedValues()
|
| Smoothed Derivatives |
public double[][][][] savitzkyGolay(int sgFilterWidthx, int sgFilterWidthy, int sgFilterWidthz, int p, int q, int r)
|
| public double[][][] getSavitzDerivatives()
|
| The Filter |
public double[][] getSGcoefficients()
|
| public void setSGpolyDegree(int degree)
|
| public int getSGpolyDegree()
|
| public int[][] getSGPolyIndices()
|
| public static double[][] savitzkyGolayFilter(int nBackwardx, int nForwardx, int nBackwardy, int nForwardy, int nBackwardz, int nForwardz, int degree)
|
| public static int[][] filterIndices(int degree)
|
| Moving Average Window |
public double[][][] movingAverage(int sgWindowWidthx, int sgWindowWidthy, int sgWindowWidthz)
|
| public double[][][] movingAverage(int sgWindowWidth)
|
| public double[][][] getMovingAverageValues()
|
| public BigDecimal[][][] movingAverageAsBigDecimal(int sgWindowWidthx, int sgWindowWidthy, int sgWindowWidthz)
|
| public BigDecimal[][][] movingAverageAsBigDecimal(int sgWindowWidth)
|
| public BigDecimal[][][] getMovingAverageValuesAsBigDecimal()
|
| Extent of smoothing |
public double extentMovingAverage()
|
| public double extentSavitzlyGolay()
|
| Interpolation |
Savitzky-Golay |
public double interpolateSavitzkyGolay(double xi, double yi, double zi)
|
| Moving average |
public double interpolateMovingAverage(double xi, double yi, double zi)
|
| Plot |
Savitzky-Golay |
x-direction section |
public double plotSavitzkyGolayX(double yValue, double zValue)
|
| public double plotSavitzkyGolayX(int yIndex, dint zIndex)
|
| y-direction section |
public double plotSavitzkyGolayY(double xValue, double zValue)
|
| public double plotSavitzkyGolayY(int xIndex, int zIndex)
|
| z-direction section |
public double plotSavitzkyGolayZ(double xValue, double yValue)
|
| public double plotSavitzkyGolayZ(int xIndex, int yIndex)
|
| Moving average |
x-direction section |
public double plotMovingAverageX(double yValue, int zValue)
|
| public double plotMovingAverageX(int yIndex, int zIndex)
|
| y-direction section |
public double plotMovingAverageY(double xValue, int zValue)
|
| public double plotMovingAverageY(int xIndex, int zIndex)
|
| z-direction section |
public double plotMovingAverageZ(double xValue, int yValue)
|
| public double plotMovingAverageZ(int xIndex, int yIndex)
|
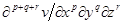
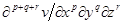
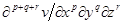 , for the data entered via the constructor arguments, using a three dimensional Savitzky-Golay filter of width sgFilterWidthx points in the x dimension, of width sgFilterWidthy points in the y dimension and of width sgFilterWidthz points in the z dimension. The arguments p, q and r contains the values of the required orders of the derivative, p, q and r. The smoothed v values are returned, in the above usage, in smoothedDataPlusDeriv[0], the derivatives are returned in smoothedDataPlusDeriv[1].
, for the data entered via the constructor arguments, using a three dimensional Savitzky-Golay filter of width sgFilterWidthx points in the x dimension, of width sgFilterWidthy points in the y dimension and of width sgFilterWidthz points in the z dimension. The arguments p, q and r contains the values of the required orders of the derivative, p, q and r. The smoothed v values are returned, in the above usage, in smoothedDataPlusDeriv[0], the derivatives are returned in smoothedDataPlusDeriv[1].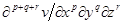 . The Savitzky-Golay derivative method must already have been called as the last derivative method and the values of p, q and r will be that used in this last call.
. The Savitzky-Golay derivative method must already have been called as the last derivative method and the values of p, q and r will be that used in this last call.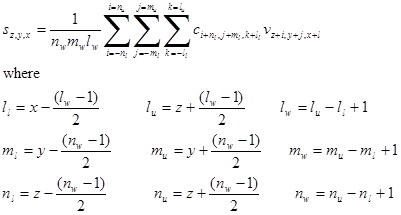
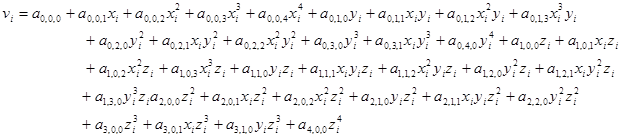
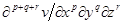 where p, q and r are given by the three subscripts of the polynomial coefficients, e.g. the zeroth row, indices 0,0,0, gives the smoothed zeroth derivative, i.e. the smoothed data values; the second row, indices 0,0,1, gives the derivatives
where p, q and r are given by the three subscripts of the polynomial coefficients, e.g. the zeroth row, indices 0,0,0, gives the smoothed zeroth derivative, i.e. the smoothed data values; the second row, indices 0,0,1, gives the derivatives 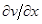 . The trio of indices associated with each row may be obtained by calling the method getSGpolyIndices() and they correspond to the indices of the coefficients of the fitting polynomial (see above). The default value of the degree of the fitting polynomial is 4. This value may be reset using the setSGpolyDegree method.
. The trio of indices associated with each row may be obtained by calling the method getSGpolyIndices() and they correspond to the indices of the coefficients of the fitting polynomial (see above). The default value of the degree of the fitting polynomial is 4. This value may be reset using the setSGpolyDegree method.