|
| INFORMATION FOR Prospective Students INFORMATION Home PROJECTS Funded QUICK LINKS Optical Devices
|
Introduction
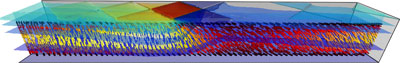
The group is dedicated to the advanced and comprehensive modelling of liquid crystal (LC) structures for displays, photonic and microwave applications. This includes modelling the switching behaviour of LCs, the hydrodynamics of LCs, the optical modelling of LC cells and the modelling of wave propagation through waveguiding structures containing LC materials. Current computer models and programs developed by the group are based on a Q-tensor representation of the liquid crystal orientation, including order variation and biaxiality, weak surface anchoring, flexoelectric effects and flow and permit the study of the dynamic behaviour of realistic 3D structures. Applications have included the analysis and design of LC on Silicon (LCOS) cells, for displays and communications, the dynamic study of bistable displays, and other devices where the dynamic behaviour of defects play an important role. The current interest is in extending these modelling capabilities further to dimensions where the current continuum theory is not adequate. This will enable us to study structures with features in the range of 10s of nm, as in LCOS cells for the future generation of displays and diffractive devices for communications (reconfigurable SLMs and holograms), reconfigurable photonic band gap structures and the inclusion of nanostructures in liquid crystal cells, as surface features or as floating, moving nanoparticles. Liquid Crystal Modelling
Capabilities; full 3D modelling, including flow, with constant or variable order, weak anchoring and the flexoelectric effect. The models support very general geometries containing multiple electrodes, dielectrics and alignment layers. Optical Modelling
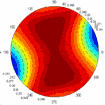
We have combined the modelling of the light through the LC layer with Ray-Tracing techniques, so that we can study complete optical systems, such as those that arise in projection displays. Device Modelling
Please see the publications section for references to more extensive studies of these devices.
This page last modified 16 April, 2010 by r.james |
NEWS |